Throughout history, some of the greatest breakthroughs in science, medicine, and technology were never patented, sold, or restricted. Instead, they were shared freely, transforming societies without demanding financial gain. These inventions given to the world for free stand as powerful reminders that generosity can shape civilization just as strongly as profit-driven innovation.

In modern times, we often associate invention with patents, intellectual property, and corporate ownership. Yet, countless life-changing ideas vaccines, communication systems, and even the internet itself were offered without barriers. This act of openness accelerated progress, allowed global access, and sometimes saved millions of lives.
Why would an inventor give up wealth and recognition for the sake of humanity? The motivations are diverse. Some innovators were guided by ethical beliefs, others valued legacy over fortune, and many simply wanted their discoveries to be used for the greater good. Regardless of the reasons, their choices reshaped the world in extraordinary ways.
In this article, we’ll explore the history of freely shared inventions, the reasons behind such decisions, and the famous innovators who placed humanity above personal gain. We’ll also look at modern open-source movements that carry this legacy forward today.
By the end, you’ll understand why some of the most valuable ideas in history belong to everyone and why these shared inventions remain some of humanity’s greatest gifts.
The Spirit Of Sharing In Human Innovation
Human innovation has always been collective. In ancient times, discoveries like fire, the wheel, and farming tools were not owned by individuals but shared openly. Knowledge was passed through oral tradition, communal teaching, and cultural exchange. Sharing knowledge was essential to survival.
As civilizations advanced, openness remained central to progress. Irrigation methods in Mesopotamia, architectural techniques in Egypt, and navigational systems from Polynesia spread across regions without ownership claims. These ideas belonged to entire societies rather than individuals.
Even during the Renaissance, when inventors like Leonardo da Vinci sketched machines and scientific concepts, much of their work was left unpatented. The notebooks of da Vinci inspired generations that followed, proving that even incomplete or freely shared ideas could influence history.
This spirit of sharing also reflected deeper cultural and moral values. Many societies viewed knowledge as a divine gift or a communal treasure. Restricting it was seen as selfish, while sharing it was celebrated as noble.
Looking back, it becomes clear that progress was often fueled not by ownership but by generosity. This same tradition laid the foundation for modern inventors who chose to release their discoveries freely, ensuring that their contributions served humanity as a whole.
Why Would An Inventor Give Away Their Work?
It may seem counterintuitive to give away something that could generate immense wealth, but history shows that many inventors had compelling reasons.
For some, the choice was moral. Jonas Salk, who developed the polio vaccine, believed that such a life-saving discovery should not be monetized. When asked who owned the patent, he famously replied, “Well, the people, I would say. Could you patent the sun?”
Others were motivated by their circumstances. Tim Berners-Lee, working at CERN when he created the World Wide Web, was not driven by financial need. Instead, he wanted to create a universal system that connected humanity. By keeping it free, he ensured that it became a truly global resource.
Some inventors distrusted the patent system itself. Nikola Tesla, for example, believed that patents could stifle innovation by limiting who could use an idea. By leaving many of his inventions unpatented or incomplete, he allowed others to build upon his work.
Legacy also played a role. Many innovators valued being remembered as visionaries more than accumulating wealth. Their reputations as pioneers of progress were reward enough.
Finally, cultural and philosophical beliefs often inspired generosity. In certain traditions, knowledge was viewed as sacred, meant to be shared rather than sold. Inventors who followed this philosophy saw themselves as stewards of progress rather than owners of it.
These diverse motivations show that invention is not always about profit. For many, the joy of contributing to humanity outweighed any financial benefit.
Famous Inventions Offered Freely To Humanity
Throughout history, some inventions stand out not only for their impact but also for the generosity behind them. These innovations were never locked away by patents or limited to a select few. Instead, they were openly shared, allowing entire societies to benefit at once. From life-saving medical breakthroughs to technologies that connect billions of people, these inventions given to the world for free prove that progress can accelerate when knowledge is treated as a public good rather than a private asset. In the following examples, we’ll explore how visionaries like Jonas Salk, Tim Berners-Lee, Nikola Tesla, and others changed humanity by choosing to share rather than profit.
Jonas Salk And The Polio Vaccine
In the early 20th century, polio was a global threat. Outbreaks paralyzed or killed thousands of children every year. When Jonas Salk developed a vaccine in 1955, he faced a monumental decision: should he patent the vaccine or give it away?
Salk chose generosity. He released the vaccine without a patent, explaining that no one should own a cure for such a devastating disease. His decision allowed the vaccine to be distributed rapidly and cheaply, saving millions of lives.
Had Salk patented the vaccine, access might have been restricted by cost or licensing agreements. Instead, he ensured that health came before profit. To this day, his name is remembered not only for his medical brilliance but also for his extraordinary humanity.
Tim Berners-Lee And The World Wide Web
The World Wide Web is so ingrained in daily life that it’s hard to imagine a world without it. In 1989, Tim Berners-Lee invented the web while working at CERN. Instead of monetizing it, he released the protocols and code to the public.
This decision sparked an information revolution. Businesses, schools, governments, and individuals gained access to a powerful communication tool without barriers. The web became the backbone of global commerce, entertainment, and education.
Berners-Lee’s choice turned a personal invention into humanity’s greatest communication platform. By refusing to patent it, he created a digital commons that continues to grow today.
Nikola Tesla And Wireless Technology
Nikola Tesla’s genius produced countless breakthroughs, from alternating current to radio waves. While he patented some inventions, many of his most ambitious ideas such as wireless energy transmission were left unpatented.
Tesla envisioned a world where electricity was transmitted freely, without wires, to every home and community. His Wardenclyffe Tower experiment aimed to prove this concept. Though financial troubles prevented its completion, Tesla’s vision inspired modern wireless technologies, including radio, Wi-Fi, and mobile communication.
By leaving much of his work open, Tesla allowed future generations to build upon his ideas. Though he died with little wealth, his legacy continues to influence nearly every aspect of modern technology.
Louis Pasteur And Pasteurization Methods
Louis Pasteur’s contributions to microbiology changed the world. His discoveries in germ theory and pasteurization revolutionized medicine and food safety. Importantly, Pasteur made his methods widely available, allowing industries around the globe to adopt them quickly.
Instead of restricting his findings, Pasteur published them openly. This decision ensured that pasteurization became a global standard, reducing foodborne illness and saving countless lives.
His willingness to share rather than profit illustrates how scientific openness accelerates progress.
Other Notable Free Inventions
Beyond these famous figures, many other inventions were shared freely.
- Open-source software like Linux and Python powers much of today’s digital infrastructure. Developers contribute freely, creating tools used worldwide.
- The printing press spread rapidly across Europe after Gutenberg’s invention, democratizing knowledge.
- Vulcanized rubber developed by Charles Goodyear eventually became widely accessible, fueling industries from transportation to manufacturing.
- Aviation advances by the Wright brothers and others quickly entered the public domain, allowing aviation to flourish.
Each of these inventions demonstrates the transformative power of sharing knowledge rather than restricting it.
Unsung Heroes: Lesser-Known Inventions Freely Given
Not all contributions came from famous names. Many lesser-known inventors offered practical tools and ideas without seeking profit.
Fire safety devices, such as early extinguishers, were often shared openly to protect communities. Household conveniences like simple cooking tools, farming equipment, and sanitation systems spread without ownership.
Medical practices, including early forms of antiseptics and surgical techniques, were passed from doctor to doctor, often without patents or restrictions. These contributions saved lives but rarely brought fame to their creators.
These unsung heroes remind us that everyday progress often depends on small, freely shared innovations. Though their names may not appear in history books, their generosity continues to improve lives.
Modern-Day “Free Inventions” And Open-Source Movements
The legacy of free invention continues today in the digital age. Open-source software, collaborative hardware, and shared designs are reshaping how we create.
Linux, an open-source operating system, powers everything from web servers to smartphones. Python, another open project, is one of the most widely used programming languages worldwide. Both thrive because they are freely shared.
Hardware projects like Arduino and Raspberry Pi give students, engineers, and hobbyists accessible tools for innovation. By remaining open, they encourage creativity and experimentation.

The maker movement embraces this spirit through 3D printing. Thousands of free designs circulate online, allowing anyone to create practical tools, toys, or replacement parts. Renewable energy projects, such as open-source solar and wind systems, also aim to make sustainability accessible worldwide.
These modern inventions given to the world for free prove that openness drives progress. Instead of limiting innovation, sharing accelerates it just as Salk, Tesla, and Berners-Lee once demonstrated.
The Impact On Society And The World
The impact of free inventions is profound. They save lives, expand access, and spark industries.
Salk’s polio vaccine nearly eradicated a disease. Berners-Lee’s web reshaped communication and commerce. Open-source software powers much of today’s digital infrastructure.
By removing barriers, free inventions accelerate adoption. They promote equity by ensuring that even underserved communities can benefit from new technologies. Moreover, industries often grow around these inventions, proving that sharing knowledge can fuel economic growth as well as humanitarian progress.
The Trade-Off: Free Invention Vs. Patented Innovation
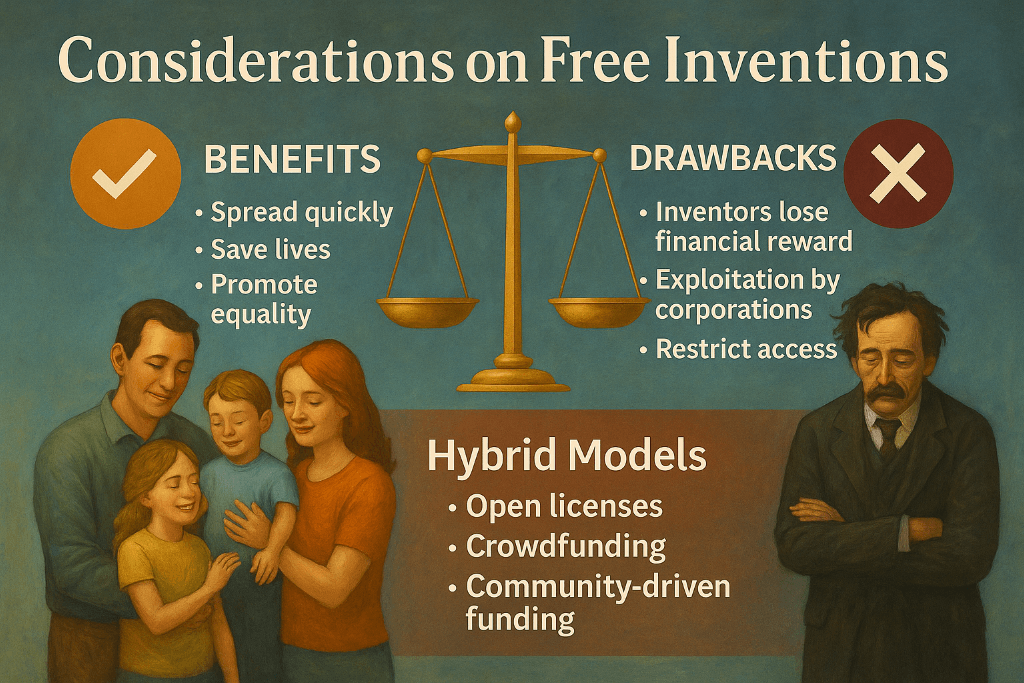
While free inventions benefit society, they also come with challenges.
On the positive side, free inventions spread quickly, save lives, and promote equality. However, inventors often lose financial reward. Jonas Salk gave up potential billions, while Nikola Tesla died in poverty.
Additionally, corporations sometimes exploit free inventions for profit without recognizing the original innovator. This raises ethical concerns about fairness and sustainability.
Patents, on the other hand, protect inventors and provide income that can fund future research. They encourage investment but also restrict access, slowing adoption.
The ideal balance may lie in hybrid models open licenses, crowdfunding, or community-driven funding that allow inventors to share freely while still receiving support.
Lessons For Future Innovators
Modern inventors can learn valuable lessons from the past.
First, innovation and generosity are not mutually exclusive. Sharing can create legacies that last centuries.
Second, new tools like open licenses and crowdfunding provide ways to share inventions while still gaining recognition or compensation.
Finally, inventors should consider the bigger picture: will their work have a greater impact if freely shared? For many, the answer is yes.
History shows that the choice to give freely can define an inventor’s legacy as much as their discovery itself.
Final Thoughts
From life-saving vaccines to the internet, free inventions have transformed the world. These contributions demonstrate that generosity is as important to progress as genius.
Inventors like Salk, Berners-Lee, Tesla, and countless others chose humanity over profit. Their decisions remind us that the most valuable gifts are often those that cannot be owned.
As we face new global challenges, supporting open innovation becomes increasingly vital. The future may depend not only on what we invent, but also on what we are willing to share.
FAQs
What Are Some Famous Inventions Given To The World For Free?
Examples include the polio vaccine, the World Wide Web, open-source software like Linux, and Nikola Tesla’s contributions to wireless communication.
Why Did Jonas Salk Refuse To Patent The Polio Vaccine?
Salk believed the vaccine should belong to humanity. His goal was to save lives, not generate profit, ensuring wide access and distribution.
How Has Tim Berners-Lee’s Invention Shaped Society?
By making the World Wide Web freely accessible, Berners-Lee accelerated global communication, commerce, and education, transforming nearly every aspect of daily life.
What Role Does Open-Source Software Play Today?
Open-source software powers much of the modern internet and technology infrastructure. Its accessibility allows collaboration, rapid development, and global innovation.
Can Inventors Still Profit While Giving Inventions Away?
Yes. Many businesses thrive by offering services, customization, or support around free inventions. For instance, Red Hat profited by building services around Linux.Can Inventors Still Profit While Giving Inventions Away?
What Are The Drawbacks Of Not Patenting Inventions?
The main drawback is financial loss for the inventor. Additionally, corporations may exploit freely shared ideas without crediting or supporting the original innovator.
How Can I Support Open Innovation Today?
You can contribute to open-source projects, fund inventors through crowdfunding, or freely share your own designs and knowledge to keep the tradition alive.
